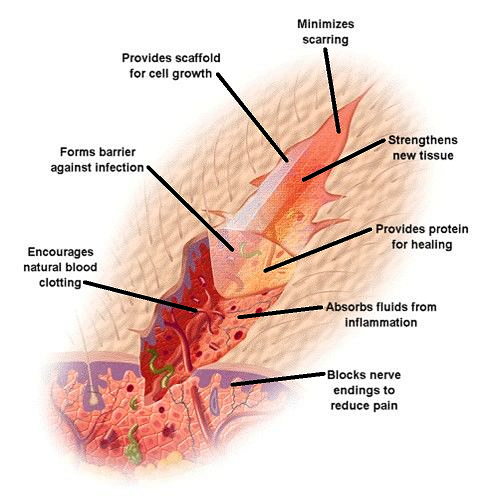
Introduction wound healing
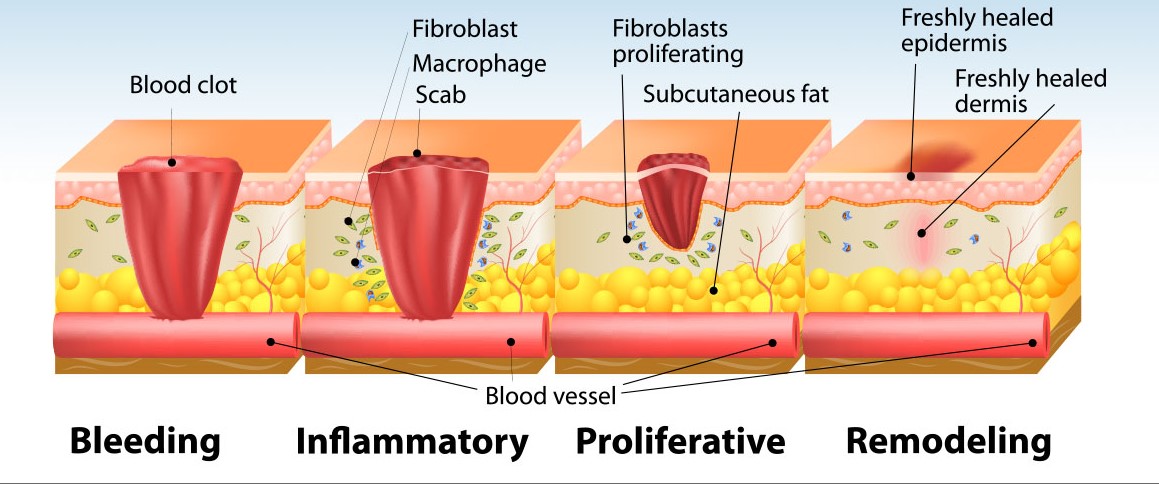
Chronic wounds have become an increasingly growing problem in the healthcare. These type of wounds cause severe pain, lead to limited physical activity and isolation, and increased dependence on care. The wound healing process consists of four phases; the Hemostatis phase, the Inflammatory phase, the Proliferative phase and the Remodelling phase.
The wound healing process is complex and can be interrupted by several factors; local and systemic factors, moisture, infection, maceration (local); age, nutritional status, body type (systemic). The wound healing processes are also affected by smoking, age, various disease states such as diabetes and hormonal factors. If these phases and processes are disturbed in any way, it will result in poor and slow wound healing.
Conventional wound treatment
Conventional wound treatment includes regular dressing changes, anti-bacterial creams, antibiotics and in extreme cases, surgery or amputation. These measures do not really solve the problem, but rather maintain it or create new problems.

Nanomedicine
Nanotechnology is about developing or changing material at nanometer level to achieve desired properties on a larger scale. The prefix nano means billionth. The area of application of nanotechnology is extensive and is expected to radically influence in basically every industrial sector, and last but not least; the medical field.
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. The area includes the use of nanoscale materials in order to diagnose, treat and monitor disease. Nanomedicine has been called a medical revolution and nanonparticles have proven to be very efficient in curing chronic wounds. There seems to be no limit to what can be aschieved with the help of nanoparticles
Our research
In our research we use a certain type of biodegradable core-shell nanoparticles incorporated into a hydrogel matrix. We have developed a method for making nanoparticles that spontaneously reassamble themselves from tailor-made macromolecules. The balance between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts are important for the nanoparticles to be formed. The hydrophobic portion makes it possible to load the particles with different molecules (such as medicine). By changing the target-seeking molecules on the surface of the nanoparticles, or by changing the size of the nanoparticles, or by introducing ionic groups, the selective uptake can be increased in different types of cells.
The nanoparticles have the ability to trap water up to thousand times their dry weight, which makes them a valid alternative for wound healing applications. The use of this type of nanoparticle-based hydrogels offer many advantages due to their high degree of biocompatibility, low cost and biodegradability.